CyberTalents - N1ght Walker
Category: Reverse Engineering
Can you find the walker secret?
Challenge : Night Walker
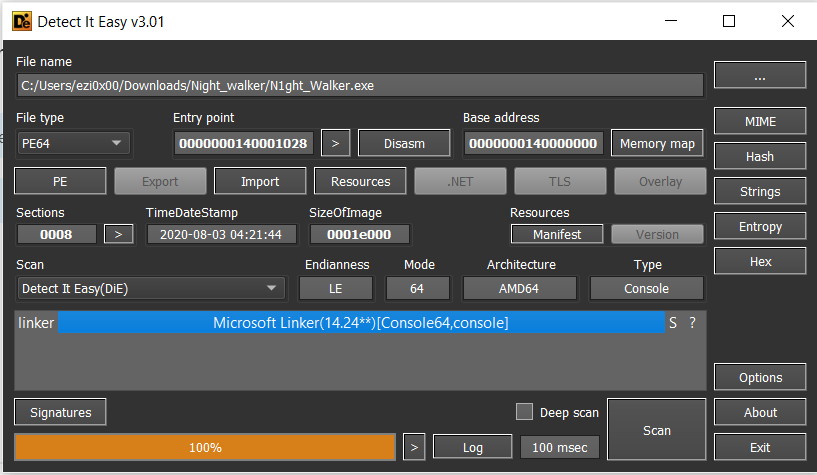
Fingerprint:
We notice we have exe file x64 bit and encrypt text file contain the flag.
in basic dynamic analysis we will notice the exe file after few seconds and some keystrokes encrypted data is written to the dropped file called
secret_log.txt.
Static Analysis:
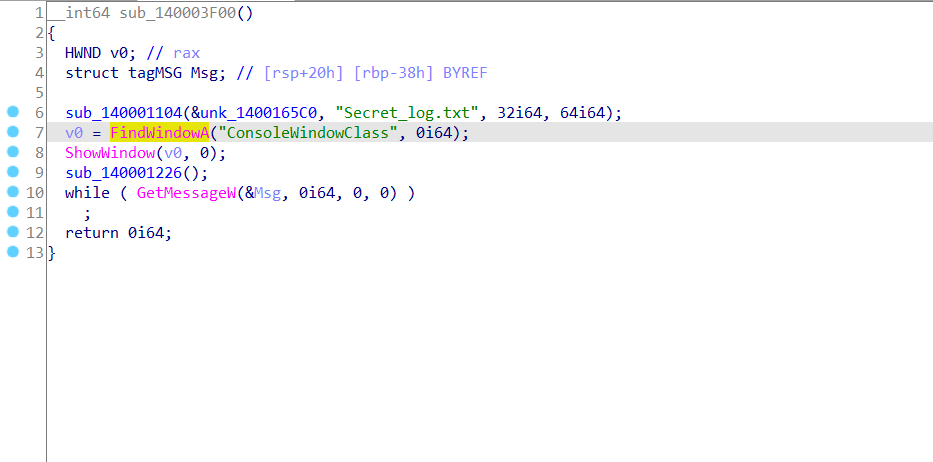
Notice in main function it call sub_140001104 function with the name of the file that will be dropped.
Call FindWindowA function it used to retrieves a handle to the top-level window whose class name and window name match the specified strings.
and call the ShowWindow function to Sets the specified windows show state, in the our case it used to hide the window and activates another window because:
BOOL ShowWindow(
HWND hWnd, //A handle to the window
int nCmdShow //Controls how the window is to be shown and in our parameters SW_HIDE 0 hide the window
//If the window was previously hidden, the return value is zero.
);
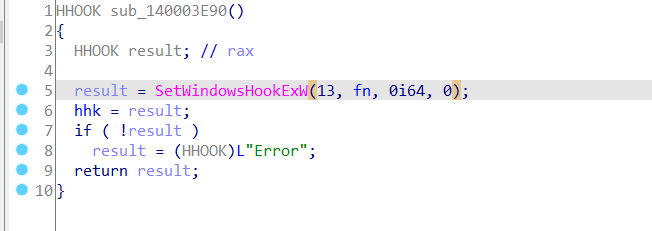
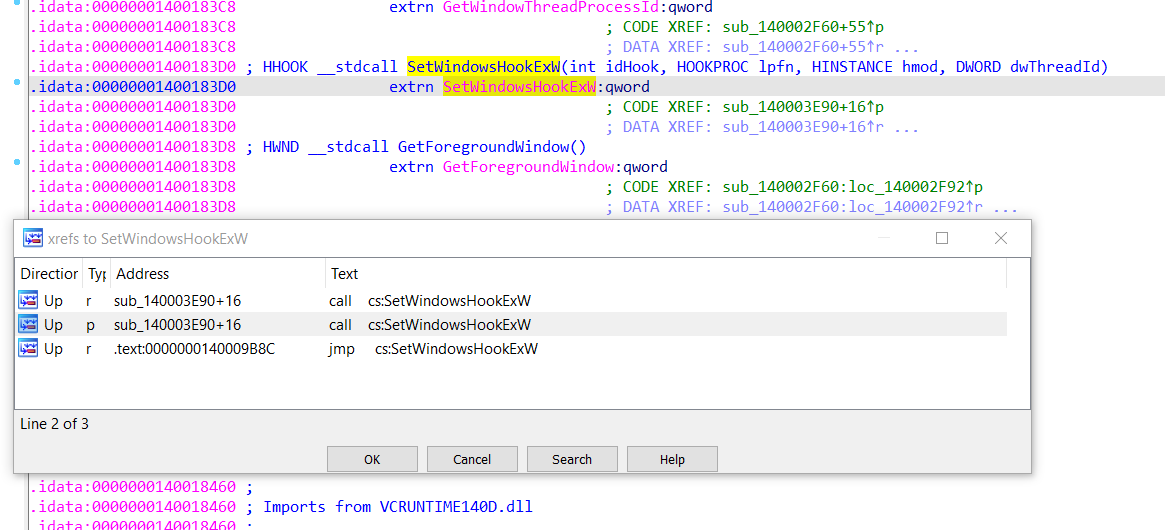
and the sub_140001226 it’s just a wrapper for the function sub_140003E90 function we will find it’s called SetWindowsHook API
 |
| 
After read the document about this function:
HHOOK SetWindowsHookExA(
int idHook,
HOOKPROC lpfn,
HINSTANCE hmod,
DWORD dwThreadId
);
the first parameter is the type by id of the hooked event and the second parameters is a pointer to the hook function.
in our case:
result = SetWindowsHookExW(13, fn, 0i64, 0);
// first parameter: 0x13 is WH_KEYBOARD_LL 13 that monitors low-level keyboard input events.
// second parameter: A pointer to the hook procedure.
The hook is monitor keyboard input events which
SCREAMS KEYLOGGER.
the challenge aslo provided a flag.txt, it did not contain any readable/printable data so it probably is the output of the keylogger after being encrypted.
as the flag.txt is the output of the binary, we should look for places in the code that uses the write function.
 |
 |
it in
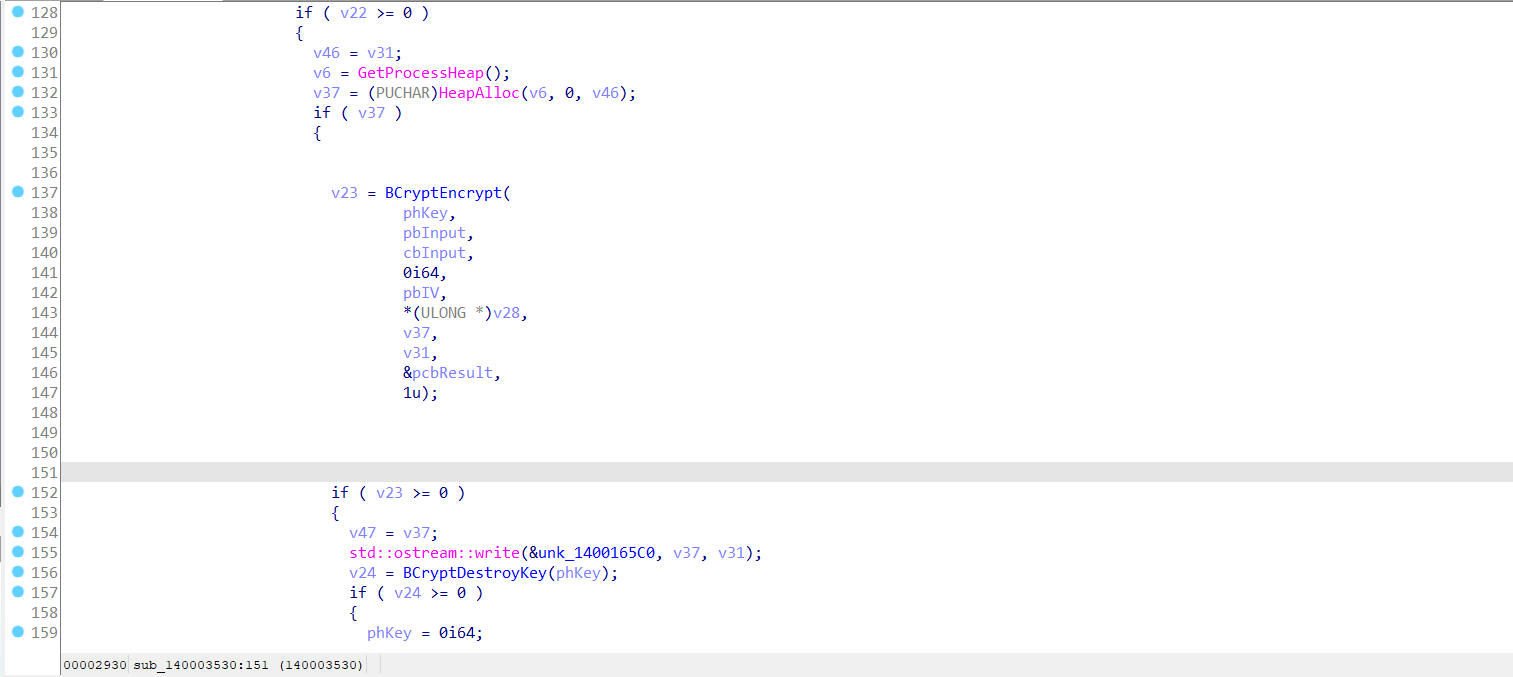
sub_140003530alot of branches it’s used to choose the corresponding char, let’s decompile and analysis it more.
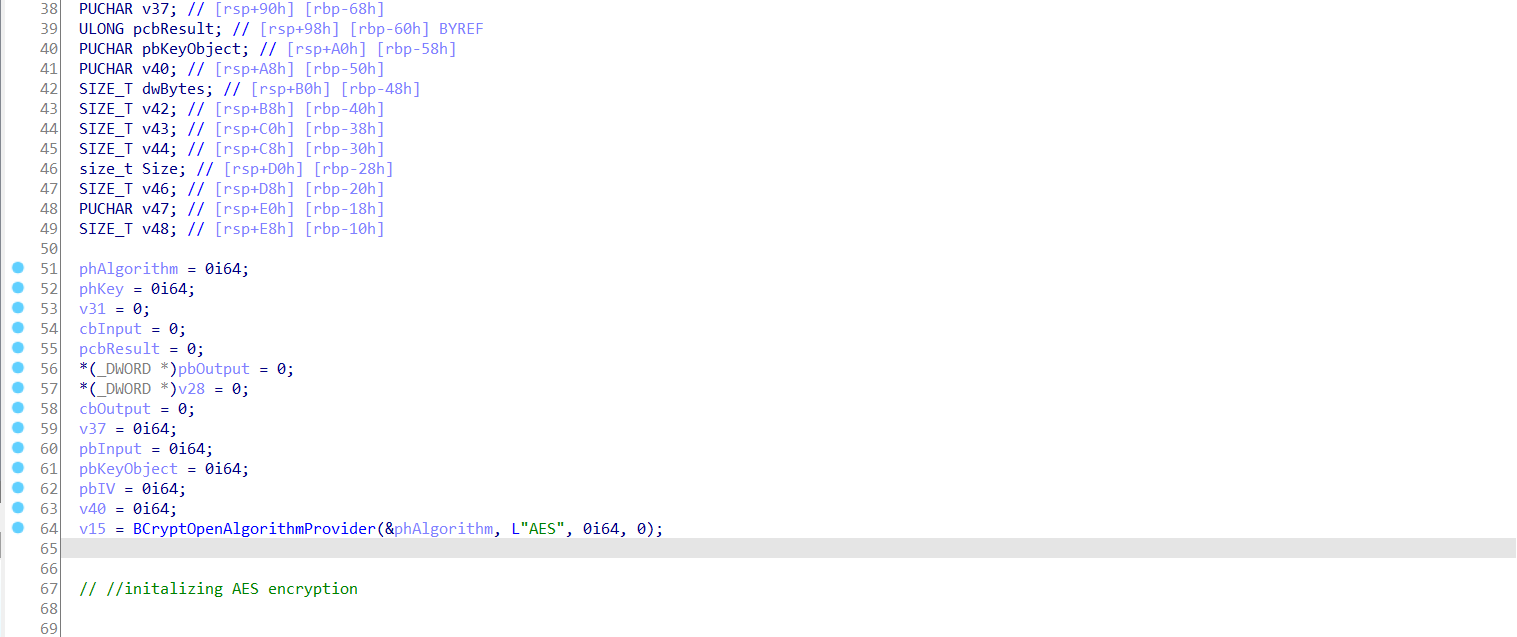
if we find the encrypt function we can figure out what key it is using, and i noticed in imports section and this function used write data there are BCryptEncrypt API
let’s understand parameters from doc:
NTSTATUS BCryptEncrypt(
BCRYPT_KEY_HANDLE hKey, //handle of key
PUCHAR pbInput, //input to be encrypted
ULONG cbInput, //len of input
VOID *pPaddingInfo,
PUCHAR pbIV, //IV
ULONG cbIV, //len of the IV
PUCHAR pbOutput,
ULONG cbOutput,
ULONG *pcbResult,
ULONG dwFlags
);
if we have the secret and the IV we can decrypt the
flag.
notice the memcpy copies some data to IV and the mode of AES encryption is CBC.
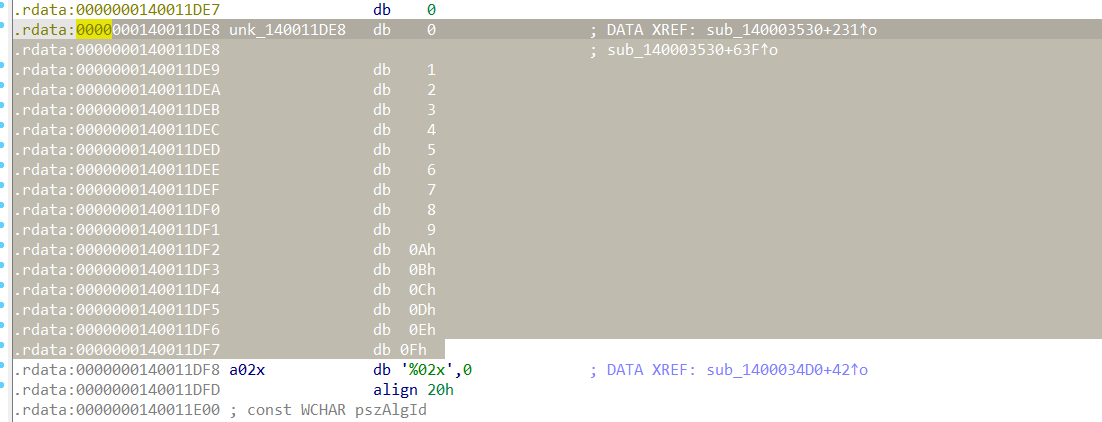
But let’s first see the IV is the most important thing, Let’s hunt the data that was copied to the IV.
IV:
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A, 0x0B, 0x0C, 0x0D, 0x0E, 0x0F
Now let’s look for the secret key.
If we go back to the document, we will see the parameter responsible for the key, The handle of the key to use to encrypt the data. that handle is obtained from one of the key creation functions, such as BCryptGenerateSymmetricKey, BCryptGenerateKeyPair , or BCryptImportKey.
in another meaning:
BCryptEncrypt generates the key from a secret then uses the key from then on, we need to find where the key from.
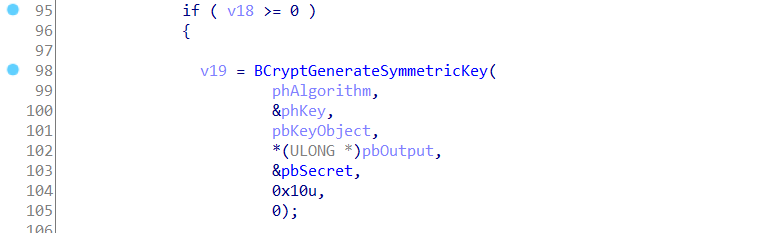
our exe used BCryptGenerateSymmetricKey to generates the key, let’s see which parameter is secret key.
NTSTATUS BCryptGenerateSymmetricKey(
BCRYPT_ALG_HANDLE hAlgorithm,
BCRYPT_KEY_HANDLE *phKey,
PUCHAR pbKeyObject,
ULONG cbKeyObject,
PUCHAR pbSecret, //here
ULONG cbSecret,
ULONG dwFlags
);
it’s 5th parameter:
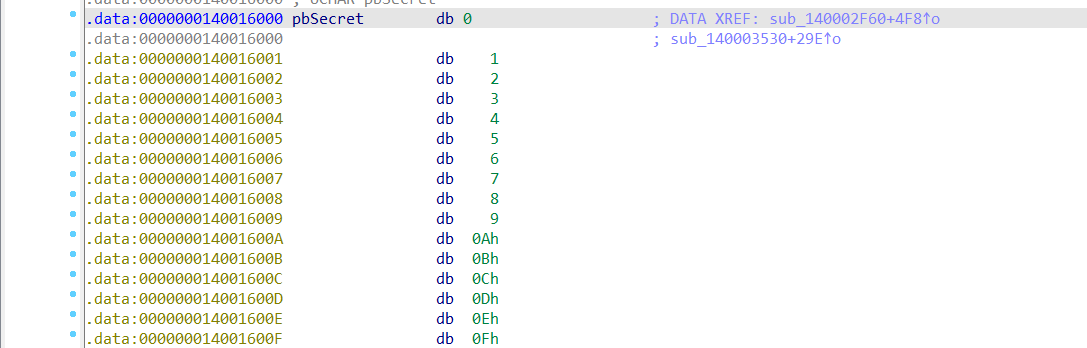
Secret Key:
0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A, 0x0B, 0x0C, 0x0D, 0x0E, 0x0F
But don’t get like a reckless ass and go write a decryption script, slow down and search well
you will notice the 5th parameter
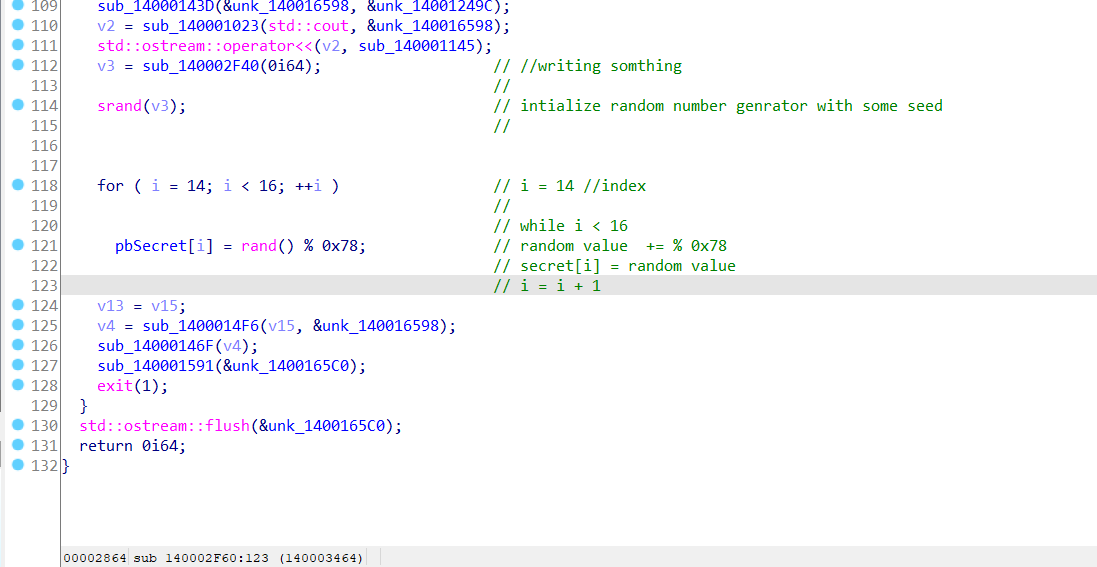
pbSecretxref to another functionsub_140002F60.
it’s modifing the secret value with a random value, luckily the random value is mod’d with 0x78 or 120 in d so the number is b/n, i does 0xe or 14 in d, 0xf or 16 in d.
Now we can bruteforce the last two bytes of key and decrypt flag.
Solution :
Script:
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import struct
key = b''.join([struct.pack("B", i) for i in range(0x10)])
IV = b''.join([struct.pack("B", i) for i in range(0x10)])
found = 0
idx = 0xe
for random_value in range(0x0, 0x78+1):
for random_value_x in range(0x0, 0x78+1):
key = [i for i in range(0x10)]
key[idx] = random_value
key[idx+1] = random_value_x
key = b''.join([struct.pack("B",i) for i in key])
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv = IV) #we noticed before in sub_140003530 function the mode is CBC
with open('flag.txt','rb') as f:
data = f.read()
ciphertext = cipher.decrypt(data)
if b"flag" in ciphertext.lower():
print(ciphertext)
found = 1
break
if found:
break
The Flag is: flag{k3y_l0gg3r_n_st34lth_m0d3}
Looking at the solution, you may find the topic is long and cumbersome, but this is just to clarify after the details. You could simply put the file on virustotal or use capa rules to know from the beginning that it is a keylogger instead of searching step by step, and when you know it is a keylogger and know how it works, you will just look at Imports section, extract the important functions and analyze them, and you will reach the desired easily
Thanks for reading, Suggestions & Feedback are appreciated !